CO-OCCURRING DISORDERS
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Do you know the origins of the term narcissistic personality disorder? The character Narcissus from Greek mythology is the basis for the term narcissism. Previously known as Narcissists, people with Narcissistic personality disorder have preoccupations with themselves and their outward appearances. They also are fixated on how others perceive them.
The Story of Narcissus
In ancient Greek mythology, a proud hunter named Narcissus was known for his handsomeness. Narcissus was drawn to anything beautiful and thrived on admiration. He also had disdain for people who loved him. Some of his loved ones committed suicide as a way of proving their unrelenting devotion to his striking appearance.

The Sadness of Echo
Narcissus broke the heart of the wood nymph Echo, who loved him, but he did not care. She then spent the rest of her sad days wandering the woods until all that remained was only her echo sound.
Nemesis Enacts Her Revenge
The goddess of revenge, Nemesis, then retaliated for Echo’s heartbreak. She lured Narcissus to a pool where he saw his reflection in the water. Not realizing he was gazing at himself, he fell in love with the image and could not pull away. Narcissus then realized it was a love that could not be returned. As a result, his fiery passion caused him to melt away until all that was left was a narcissus flower.
Narcissistic Personality Disorder Defined
There is no single factor that can be considered a causative agent of bipolar disorder. However, bipolar disorder is an interplay of many factors that trigger its onset. Current research has kept the focus on the biological causes of bipolar disorder, which include genetic causes, neurohormonal causes, and difference observed in the brain structure of affected individuals.4 Other causes include psychosocial foundations and the environment of the individual.
Narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) is a recognized personality disorder. NPD is listed in the DSM-5, a manual of mental disorders published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). Narcissistic personality disorder is defined as a disorder that displays:
• A pattern of appearing or trying to appear more valuable than is the case
• A need for admiration
• A lack of empathy
Narcissistic personality disorder is a mental condition where individuals have an inflated sense of their importance. They also have a deep-seated need for lots of attention and admiration from those around them. People with narcissistic personality disorder have troubled relationships and a lack of empathy for others. They display bravado to the world but secretly struggle with self-esteem, which is frequently shattered with the slightest criticism. People with this type of disorder suffer greatly; having trouble with jobs, relationships, and social interactions. There is no such thing as constructive criticism for a sufferer of narcissistic personality disorder; even the most friendly advice will crush their self-esteem.
NARCISSISTIC PERSONALITY DISORDER
Symptoms
Excessive Sense of Self-Importance
NPD sufferers feel an exaggerated sense of how important and unique they are. They also set hard to reach goals in front of others to emphasize how “special” they are so others approve of them.
Lack of Empathy
Not being able to recognize or identify with the feelings and needs of others is a major sign of narcissistic personality disorder.
Reactions to Others
People with NPD can tune in to the reactions of others, but only if they perceive them as being relevant to themselves.
Reactions to Others
People with NPD can tune in to the reactions of others, but only if they perceive them as being relevant to themselves.
Defensiveness
The defenses that people with narcissistic personality disorder throw up around them often put strains on personal relationships. These defenses often lead to isolation. Narcissists need support, love, and respect from others to maintain their inflated self-image. Thus, when their actions alienate others, they suffer immensely. Feelings of isolation and abandonment can result. Slight criticisms that others regard as harmless provoke narcissists to react, often to their detriment.
NARCISSISTIC PERSONALITY DISORDER
Side Effects
Despite an inflated sense of importance and self-confidence, there are unfortunate consequences to having narcissistic personality disorder.
Sensitivity
People with narcissistic personality disorder have extremely fragile self-esteem. They are easily injured when they meet with criticism or defeat.
Shame
People with narcissistic personality disorder may also experience higher levels of shame and humiliation from emotional instability.
Depression
A common symptom of narcissistic personality disorder is depression due to the perception of emotional injury from others and social isolation.
Narcissistic Personality Disorder Checklist
The following is a comprehensive list of narcissistic personality disorder behaviors and characteristics. Don’t be concerned if you can relate to a few of them. People with narcissistic personality disorder consistently display most of these items at different levels of severity. People with narcissistic personality disorder can:
- Possess an overstated sense of self-importance
- Display a sense of entitlement
- Exaggerate their talents and achievements
- Need constant, excessive admiration
- Believe in their superiority, so they can only socialize with special people that are their equals
- Have expectations of special favors
- Have expectations of people complying with their wishes without question
- Expect recognition as being superior or special without the achievements that would call for these conclusions
- Have a preoccupation with power, success, beauty, or the perfect partner
- Dominate conversations
- Look down or insult people they perceive as “unequal” or inferior
- Be unable or unwilling to recognize or identify with the needs and feelings of others
- Take advantage of others to get what they want
- Come across as arrogant, self-centered, cocky, stuck-up, and pretentious
- Show envy and feel others envy them
- Believe they must have the best of everything
RESPONSES
People with narcissistic personality disorder can also have problems dealing with anything perceived as disapproval or fault-finding. In response, they can:
- Quickly feel slighted at things others consider harmless
- Belittle others to make themselves appear more accomplished
- Have a hard time controlling their emotions and behavior
- React impatiently or angrily when special treatment doesn’t happen
- Experience serious personal problems
- Feel moody and depressed because they are not “perfect”
- Strike back with extreme anger, rage, or contempt to prove they are superior to others
- Have major problems dealing with stress and change
- Secretly harbor feelings of shame, insecurity, humiliation, and vulnerability
Causes of Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Conditional self-love is at the core of NPD. Individuals feel that they must be important, unique, and entitled to have worth. Studies show that conditional self-love usually develops during school years and carries on through adulthood.
FREUD’S THEORY
Sigmund Freud believed that people with narcissistic personality disorder suffered some sort of arrested development as infants. Freud said that all infants are naturally selfish. Infants focus on having their needs met by others. To do so, they adapt their behavior with others to have their needs met. Some children do not outgrow these types of behaviors. They can then develop NPD that persists throughout adulthood.
KOHUT’S THEORY
Heinz Kohut is a noted psychoanalyst. He proposed that childhood arrested development comes from a complex child-parent relationship. Specifically, it stems from parents who focus on the importance of a child’s appearance or achievements. It also involves parents who reinforce a child’s sense of self that depends on their child’s performance compared to others. In other words, to be worthy means being the best. As these children age, they focus on how they appear to others. This focus leads to avoiding others to hide any internal weaknesses. They also avoid others to hide their low self-esteem. This emphasis causes children to be highly critical of perceived flaws in themselves and others. Low self-esteem leads to an unquenchable need to reinforce a positive self-image.
Statistics
In the United States, it is estimated that: Narcissistic personality disorder is more prevalent among black men and women and Hispanic women. Narcissistic personality disorder is also more prevalent among younger adults. NPD is found more among the separated, divorced or widowed, and adults who never married. There is a high co-occurrence of substance use, mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and other personality disorders for people with NPD. There is a relationship between narcissistic personality disorder and phobias, generalized anxiety disorder and bipolar disorder, especially for women. There is a relationship between narcissistic personality disorder and alcohol abuse and dependence, drug abuse and dependence, as well as obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD).

Connection Between NPD and Addiction
Living with or around a person with narcissistic personality disorder may not be easy. It can also have serious consequences for the NPD sufferer caught in a loop. They try to be perfect. In the process, they alienate those around them while trying to maintain an impossible image and standards. There is a significant relationship between narcissistic personality disorder and addiction. One research study showed that:
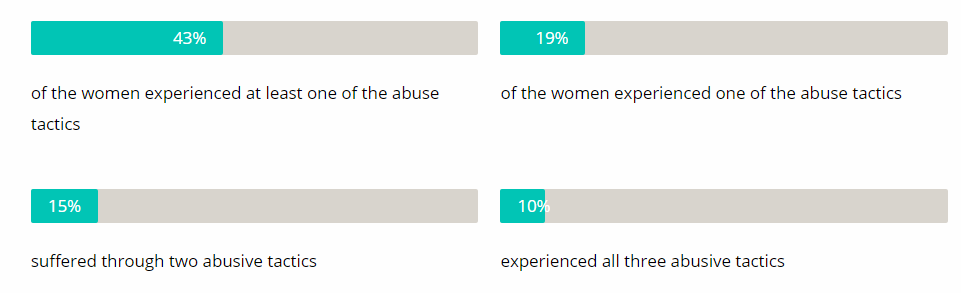
Substance Use
The connection between substance use and narcissistic personality disorder can be from:
• People with NPD attempting to restore or maintain an inflated sense of self-importance.
• When narcissistic personality disorder sufferers encounter unavoidable limitations, they get depressed. Substance use could be a defensive reaction against the effects of depression.
• Aging that affects one’s appearance can also cause people with NPD to become defensive.
• The social isolation NPD sufferers experience can lead to substance abuse or dependence.
These factors can lead someone with narcissistic personality disorder to self-medicate. Using substances can make them feel like they can maintain a sense of superiority and invincibility. However, substance abuse frequently worsens mental health. Self-medication may also be related to blocking out feelings of sadness, depression, and guilt that come from not measuring up to impossibly high standards of perfection.
WHEN SHOULD A PERSON SEEK TREATMENT FOR NPD?
People with NPD may not want to believe that anything could be wrong, so they don’t see any need for treatment. If they do seek treatment, it probably won’t be for NPD symptoms. It is more likely they will seek treatment for drug or alcohol use, depression, or another mental health problem. Treatment for addiction or other mental health problems may fail if NPD is not recognized and part of the treatment plan because when the patient perceives insults to their self-esteem, it becomes hard to accept and follow through with treatment.
If you:
- Recognize aspects of your personality are related to NPD
- Are abusing drugs or alcohol
- Have overwhelming feelings of sadness, isolation, or anxiety
Then consider talking to a doctor or mental health provider you trust. Getting the right treatment can help make your life easier to handle, more rewarding, and more enjoyable.
Dual Diagnosis: Frequent Co-occurring Illnesses
PSYCHOTHERAPY
Psychotherapy is “talk therapy.” Therapy takes places within a client-therapist relationship built on trust. A competent therapist recognizes it is not enough to imagine what feelings a person with NPD has. Rather, they can feel what the client feels in a certain situation. This understanding helps the client develop healthier ways of thinking and behaving.
Why Talk Therapy Works
Supportive psychotherapy builds a strong alliance between the client and counselor. The empathy the client receives from the therapist can help fill the void of empathy the client has. Positive experiences happening between client and counselor encourages the client to develop empathy as well.
COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY (CBT)
People with NPD have persistent patterns of disturbed thinking. For example, they abnormally perceive themselves or others. They may have extreme reactions to others. They can experience social isolation and personal relationship problems.
CBT addresses these many issues by changing beliefs and behaviors that are harmful. CBT does this by using:
Cognitive Restructuring:
Helps the client recognize thinking that leads to negative consequences
Behavior Changes:
Helps change behaviors that lead to negative experiences, relationship problems, and isolation.
Exposure:
Over time, the client is exposed to fearful situations to learn how to become less sensitive.
Education:
The therapist provides education and information related to the mental health issues the client experiences.
Skills Training:
Social skills are learned and practiced by the client through role-playing sessions.
Why CBT Works:
Clients with NPD get a better understanding of their behavior that bothers others. They also learn to identify how they act affects the quality of their relationships. Clients learn how to change their improper understandings and beliefs. This helps them become better adjusted and live more fulfilling lives.
MEDICATIONS
While there are no specific drugs for NPD treatment, there are medications that can help relieve some symptoms.
Why Medication Works
Medications can help relieve symptoms related to anxiety and depression. These drugs can help put NPD sufferers in better frames of mind to work on other NPD issues.
SAFE HARBOR TREATMENT CENTER
Recognizing and Treating Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Many people who live with NPD may not be aware of how it affects their well-being or their need for treatment. Left untreated, NPD sufferers deal with limited abilities and stunted potentials. NPD has social and psychological impacts due to off-putting behaviors which damage relationships. Despair, isolation, loneliness, or sadness may feel like the norm, but that does not have to be the case. There is hope and healing with the right treatment. Getting professional help provides the best tools and resources needed for recovery.
Resources
- https://books.google.com/books?id=-JivBAAAQBAJ&lpg=PA1&dq=narcissistic&pg=PA1#v=onepage&q=narcissistic&f=false
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4664566/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18557663
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2860525/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3138327/




